Trong bài viết dưới đây mình sẽ giải lại các bài tập trên CryptoHack bằng ngôn ngữ C++. Mục đích của bài này là để ghi chú và luyện tập là chủ yếu nên có gì mọi người hoan hỉ nhé.
Nội dung chính mà bài viết sẽ xoay quanh:
- CryptoPP, NTL, GMP, primesieve - các thư viện số học, crypto trong C++
- Ngôn ngữ lập trình C++
- Math/Crypto
Doc cho thư viện CryptoPP:
Note: Chỉnh lại file task.json một chút để làm việc với CryptoPP. Ngoài ra mình có cài sẵn gmp và ntl để làm các bài tập sau này:
{
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"type": "cppbuild",
"label": "C/C++: build with local CryptoPP",
"command": "/usr/bin/g++",
"args": [
"-std=c++20",
"-fdiagnostics-color=always",
"-Wall",
"-Wextra",
"-Wpedantic",
"-g",
"${file}",
"-o",
"${fileDirname}/${fileBasenameNoExtension}",
"-lntl",
"-lgmpxx",
"-lgmp",
"-lcryptopp",
],
"options": {
"cwd": "${fileDirname}"
},
"problemMatcher": ["$gcc"],
"group": { "kind": "build", "isDefault": true },
"detail": "Build with local"
}
]
}General
ASCII
Solve script:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
vector<int> a = {99, 114, 121, 112, 116, 111, 123, 65, 83, 67, 73, 73, 95, 112, 114, 49, 110, 116, 52, 98, 108, 51, 125};
string flag = "";
for (size_t i = 0 ; i < a.size();i++){
flag += char(a[i]);
}
cout << flag << endl;
return 0;
}Trong C++ để lưu “một” kí tự thì ta sử dụng kiểu dữ liệu char. Mỗi kí tự mà ta thường sử dụng đều có mã ASCII tương ứng. Char có thể lưu dữ liệu với kích thước là 1 byte và phạm vị giá trị có thể lưu là -128 đến 127.
Ở đây thì mình ép từ int sang char để đưa về chuỗi kí tự.
Hex
Bài này thì yêu cầu ta chuyển một đoạn mã hex sang bytes.
Mình thử xài thư viện cryptopp/hex.h của CryptoPP và làm tới đây thì gặp lỗi như này:
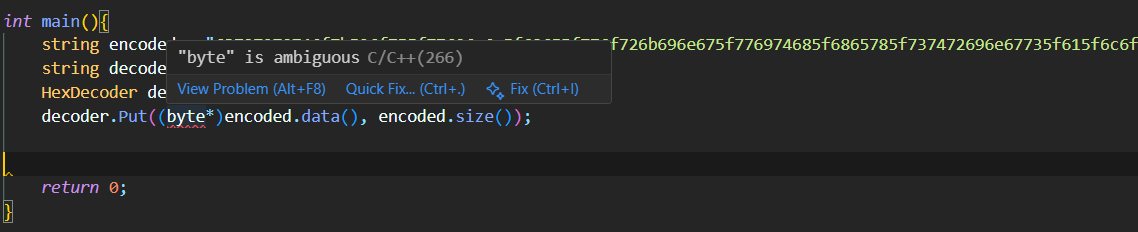
Lỗi này xảy ra do xung đột định danh giữa byte trong std::byte và CryptoPP::byte
Cách fix thì mọi người có thể đọc qua tại wiki của CryptoPP https://www.cryptopp.com/wiki/Std::byte
Ta chỉ cần chuyển thành CryptoPP::byte* là oke.
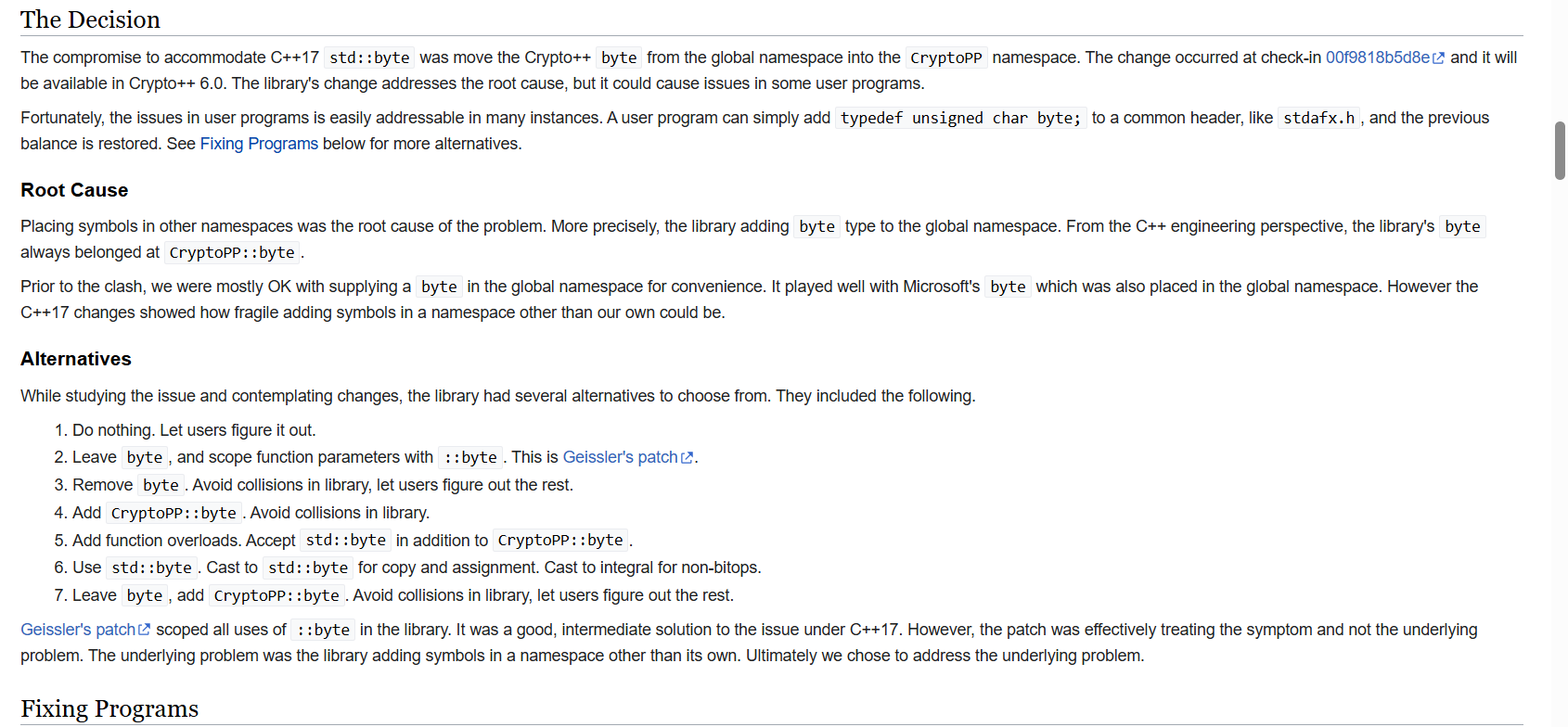
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <cryptopp/hex.h>
using namespace CryptoPP;
using namespace std;
int main(){
string encoded = "63727970746f7b596f755f77696c6c5f62655f776f726b696e675f776974685f6865785f737472696e67735f615f6c6f747d";
string decoded;
HexDecoder decoder;
decoder.Put((CryptoPP::byte*)encoded.data(), encoded.size());
decoder.MessageEnd();
word64 size = decoder.MaxRetrievable();
if(size && size <= SIZE_MAX)
{
decoded.resize(size);
decoder.Get((CryptoPP::byte*)&decoded[0], decoded.size());
}
cout << decoded;
return 0;
}Ngoài cách trên ra ta còn có thể sử dụng StringSource và StringSink của CryptoPP
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <cryptopp/hex.h>
#include <cryptopp/filters.h>
using namespace CryptoPP;
using namespace std;
int main(){
string encoded = "63727970746f7b596f755f77696c6c5f62655f776f726b696e675f776974685f6865785f737472696e67735f615f6c6f747d";
string decoded;
StringSource ss(encoded, true, new HexDecoder(
new StringSink(decoded)
)
);
cout << decoded;
return 0;
}Có một vấn đề khá thú vị trong CryptoPP đó là Pipeline API.
Về phần này mọi người có thể tham khảo ở đây:
Pipelining
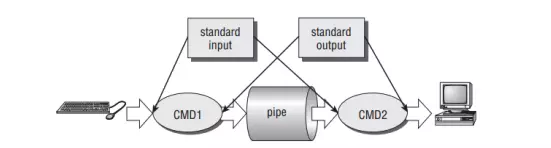
Pipelining của CryptoPP được thiết kế dựa trên Unix pipe system. Để hiểu hơn về nó thì trước tiên ta cần tìm hiểu xem Unix pipe system hoạt động như thế nào.
Pipe có thể hiểu là một kênh truyền dữ liệu giữa các tiến trình với nhau, dữ liệu xuất (stdout) của tiến trình này được chuyển đến làm dữ liệu nhập (stdin) của tiến trình kia.
Base64
Dùng cryptopp/base64.h
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <cryptopp/hex.h>
#include <cryptopp/filters.h>
#include <cryptopp/base64.h>
using namespace CryptoPP;
using namespace std;
int main(){
string encoded = "72bca9b68fc16ac7beeb8f849dca1d8a783e8acf9679bf9269f7bf";
string decoded;
string output;
StringSource ss(encoded, true, new HexDecoder(
new StringSink(decoded)
)
);
StringSource(decoded, true,
new Base64Encoder(new StringSink(output),
false));
cout << output << endl;
return 0;
}Bytes and Big Integers
Đối với bài này thì trong thư viện Pycryptodome của Python có cung cấp cho ta 2 hàm là bytes_to_long và long_to_bytes.
Trong C++ thì không như vậy. Vấn đề bây giờ là xử lý BigNum trong C++.
Với các số nguyên không quá lớn thì ta có thể làm như sau:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
unsigned long long bytes_to_long(const vector<unsigned char>& bytes){
unsigned long long result = 0;
for (unsigned char b: bytes){
result = (result << 8) | b;
}
return result;
}
vector <unsigned char> long_to_bytes(unsigned long long value){
vector <unsigned char> bytes;
while (value > 0){
bytes.push_back(value & 0xFF);
value >>= 8;
}
reverse(bytes.begin(), bytes.end());
return bytes;
}
int main() {
string s = "Hello";
vector <unsigned char> v(s.begin(),s.end());
long long res= bytes_to_long(v);
cout << res ;
return 0;
}Nhưng vấn đề ở đây là đề bài cho ta 11515195063862318899931685488813747395775516287289682636499965282714637259206269
Kiểu dữ liệu unsigned long long trong C++ chỉ biểu diễn giá trị tối đa từ 0 tới 18446744073709551615.
Cách xử lý ở đây là xài thư viện Integer.h của CryptoPP. Mọi người tham khảo mục “Encoded as Byte Array” tại đây https://www.cryptopp.com/wiki/Integer
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <cryptopp/integer.h>
using namespace std;
using namespace CryptoPP;
Integer bytes_to_long(const vector<CryptoPP::byte> &bytes){
return Integer(bytes.data(),bytes.size());
}
vector<CryptoPP::byte> long_to_bytes(const Integer &n){
size_t len = n.MinEncodedSize();
vector<CryptoPP::byte> v(len);
n.Encode((CryptoPP::byte*)&v[0], v.size(), Integer::UNSIGNED);
return v;
}
int main() {
Integer n("11515195063862318899931685488813747395775516287289682636499965282714637259206269");
vector <CryptoPP::byte> V = long_to_bytes(n);
for (auto c: V){
cout << c;
}
return 0;
}Encoding Challenge
Trong Python ta có thể sử dụng pwntools để làm bài này nhưng trong C++ thì không đơn giản như vậy. Ta cần tìm hiểu một số thư viện để làm việc và tương tác với TCP Server.
XOR Starter
Trước tiên ta nói qua về bit manipulation trong C++ và phép XOR
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s = "label";
size_t n = s.size();
cout << n;
vector <int> v;
for (auto c: s){
cout << c << endl;;
v.push_back(int(c));
}
for (auto val: v){
cout << val << " " << endl;
}
vector <int> flag;
for (auto c:v){
int val = c ^ 13;
flag.push_back(val);
}
for (size_t i = 0; i<flag.size(); i++){
cout << flag[i] << " ";
}
string flag_bytes = "";
for (size_t i = 0 ; i<flag.size(); i++){
flag_bytes += char(flag[i]);
}
cout << flag_bytes;
return 0;
}XOR Properties
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <cryptopp/hex.h>
#include <cryptopp/filters.h>
using namespace std;
using namespace CryptoPP;
std::string XorCipher(const std::string& text, const std::string& key){
std::string res = text;
for (size_t i = 0; i < text.length(); ++i){
res[i] = text[i] ^ key[i % key.length()];
}
return res;
}
int main(){
string key1 = "a6c8b6733c9b22de7bc0253266a3867df55acde8635e19c73313";
string key1_key2 = "37dcb292030faa90d07eec17e3b1c6d8daf94c35d4c9191a5e1e";
string key2_key3 = "c1545756687e7573db23aa1c3452a098b71a7fbf0fddddde5fc1";
string flag_key1_key2_key3 = "04ee9855208a2cd59091d04767ae47963170d1660df7f56f5faf";
string bytes_key1;
string bytes_key1key2;
string bytes_key2key3;
string flag_key;
StringSource(key1, true, new HexDecoder(
new StringSink(bytes_key1)
));
StringSource(key1_key2, true, new HexDecoder(
new StringSink(bytes_key1key2)
));
StringSource(key2_key3, true, new HexDecoder(
new StringSink(bytes_key2key3)
));
StringSource(flag_key1_key2_key3, true, new HexDecoder(
new StringSink(flag_key)
));
string ori_key2 = XorCipher(bytes_key1, bytes_key1key2);
string ori_key3 = XorCipher(ori_key2, bytes_key2key3);
string ori_flag = XorCipher(XorCipher(XorCipher(flag_key,bytes_key1), ori_key2),ori_key3);
cout << ori_flag << endl;
return 0;
}Favourite byte
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <cryptopp/hex.h>
#include <cryptopp/filters.h>
using namespace std;
using namespace CryptoPP;
std::string XorCipher(const std::string& text, const std::string& key){
std::string res = text;
for (size_t i = 0; i < text.length(); ++i){
res[i] = text[i] ^ key[i % key.length()];
}
return res;
}
string xorWithByte(const string& text, unsigned char key) {
string res = text;
for (size_t i = 0; i < text.size(); ++i) {
res[i] = text[i] ^ key;
}
return res;
}
int main(){
string prefix = "crypto{";
string encrypted = "73626960647f6b206821204f21254f7d694f7624662065622127234f726927756d";
string enc;
StringSource(encrypted, true, new HexDecoder(
new StringSink(enc)
));
for (int k = 0; k<256; k++){
unsigned char key = static_cast<unsigned char>(k);
const auto flag = xorWithByte(enc, key);
if (flag.starts_with(prefix)){
cout << flag;
}
}
return 0;
}Trong C++20 trở lên có hàm starts_with để check prefix